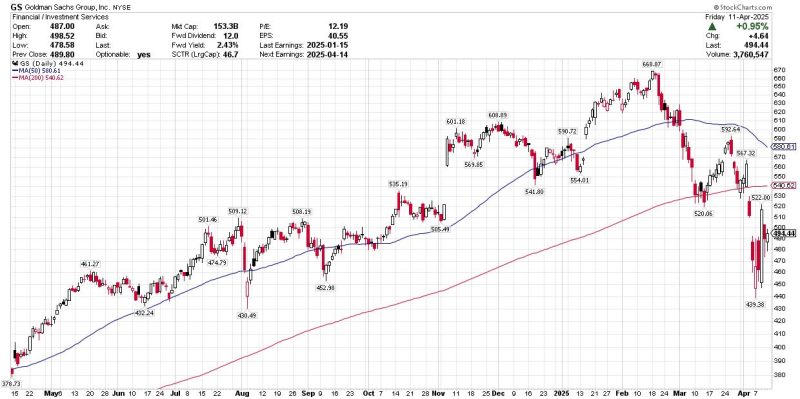
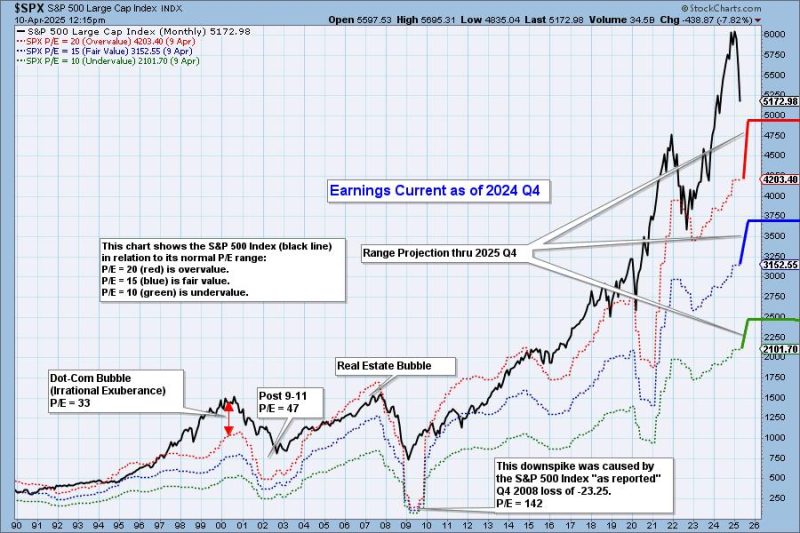
In 2024-2025, the United States significantly escalated its trade conflict with China through new tariffs, including a substantial 100% tariff on electric vehicles and 50% on essential technologies like semiconductors and solar products. These measures amplify the existing trade tensions and represent a profound shift towards economic decoupling between the two largest global economies. This article evaluates both short-term and long-term economic impacts of these tariffs, analyzing their implications for global trade patterns and specifically examining India’s potential to capitalize on these shifting dynamics.
Read the full note here
Milan Vaishnav, CMT, MSTA
Consulting Technical Analyst